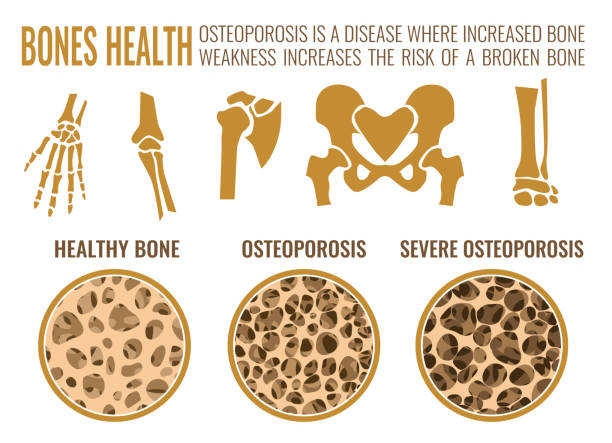
Bone is a dynamic active organ, in contrast to being a dormant tissue, which is common myth. Bone health is determined by Calcium, Vitamin D, Magnesium and Phosphorus compounds. Osteoporosis is defined as decreased bone quantity and quality.
Risk factors for osteoporosis:
- Aging, esp postmenopausal
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Endocrine diseases – Cushing’s Disease, Hyperparathyroidism
- Kidney failure
- Drugs , Esp Steroids
- Genetic causes.
Calcium balance is tightly regulated in the body, along with magnesium and phosphorus by three hormones mainly i.e. PTH (parathyroid hormone), Vitamin D, calcitonin. Bones are the main reservoir for calcium, and 99% of body calcium is present here . 1% is present in the bones in the ionized form. It is ionized calcium which is balanced by these hormones. This ionized calcium is important for Muscle contraction and nerve conduction.
Calcium is mainly absorbed from the small intestine, appro. 300mg per day, out of which 150mg is lost per day. Therefore a net balance of 150mg per day is maintained. 98%of the calcium filtered into the tubules is reabsorbed, in the kidney.
Organs involved in Calcium and Vitamin D balance in the body
- Bone
- Kidney
- Skin
- Gut ( intestines)
- Liver
- Parathyroid gland ( parathyroid hormone)
- Thyroid Gland (calcitonin)
